Understanding the IPO Market in India: A Beginner’s Guide
Imagine you run a successful manufacturing factory and need more money to open new factories. An IPO could be your answer! It’s like inviting people to invest in your company by buying small slices of ownership (shares). This guide will explain how IPOs work in India, so you can be like that factory owner and others, raising funds or even becoming an investor yourself!
How Does the IPO Market Work in India?
The IPO process in India involves several key stages:
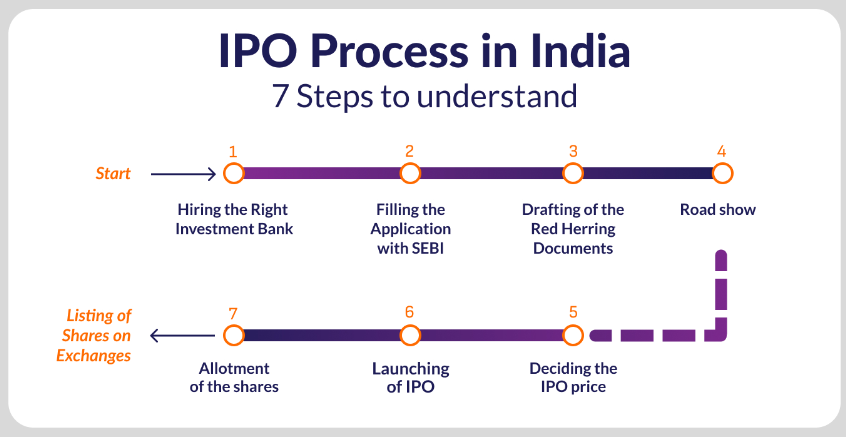
Types of IPO
There are two common types of IPO. They are-
1) Fixed Price Offering
Fixed Price IPO can be referred to as the issue price that some companies set for the initial sale of their shares. The investors come to know about the price of the stocks that the company decides to make public.
The demand for the stocks in the market can be known once the issue is closed. If the investors partake in this IPO, they must ensure that they pay the full price of the shares when making the application.
2) Book Building Offering
In the case of book building, the company initiating an IPO offers a 20% price band on the stocks to the investors. Interested investors bid on the shares before the final price is decided. Here, the investors need to specify the number of shares they intend to buy and the amount they are willing to pay per share.
The lowest share price is referred to as the floor price, and the highest stock price is known as the cap price. The ultimate decision regarding the price of the shares is determined by investors’ bids.
Let’s Understand Mainboard and SME IPOs
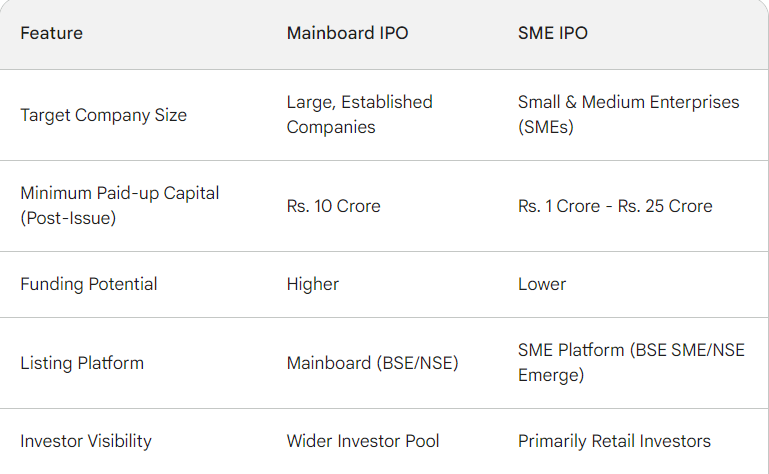
By understanding the distinction between Mainboard and SME IPOs, you can make a more informed decision about which companies you might be interested in as an investor. To gain more guidance on choosing a suitable IPO click here.
Benefits of Investing in an IPO
Investing in an initial public offering withholds the below-mentioned advantages-
- Increased Recognition
When weighing the advantages and disadvantages of an IPO, this good factor comes out on top. It assists management in gaining more reputation and credibility by becoming a trustworthy organization.
Companies that are publicly traded are typically more well-known than their private competitors. In addition, a successful process attracts media attention in the financial sector.
- Access to Capital
A corporation may never receive more capital than it raises by going public. A company’s growth trajectory might be substantially altered by the substantial cash available. An ambitious company may enter a new period of financial stability following its IPO.
This decision can help R&D, hire new employees, establish facilities, pay off debt, finance capital expenditures, and purchase new technologies, among other things.
- Diversification Opportunity
When a corporation becomes public, its shares are traded on an exchange amongst investors. This increases investor diversity because no single investor owns a majority of the company’s outstanding stock. As a result, purchasing stock in a publicly listed company can help diversify investment portfolios.
- Management Discipline
Going public encourages managers to prioritize profitability over other objectives, such as growth or expansion. It also makes contact with shareholders easier because they can’t hide their issues.
- Third-Party Perspective
When a company goes public, it gains an independent perspective on its business model, marketing strategy, and other factors that could hinder it from becoming profitable.
Conclusion
The IPO market in India offers a gateway for companies to raise capital and for investors to participate in the growth of promising businesses. By understanding the process and conducting thorough research, you can make informed investment decisions in the exciting world of IPOs.

