Loan Against Mutual Funds: Discover the Easiest Way to Get Money Now
Life often throws financial curveballs, and in such moments, quick access to cash becomes essential. Instead of redeeming your mutual fund units which can disrupt your long-term goals and trigger capital gains tax you can consider a smarter option: a Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF).
This innovative solution allows you to unlock liquidity without selling your investments. In this article, we’ll explore how LAMF works, its pros and cons, and whether it suits your financial needs.
What is a Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF)?
A Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF) allows you to borrow money against the value of your existing mutual fund holdings. Consider it a loan using your mutual fund units as collateral. You don’t sell your investments; instead, you pledge them as security for the loan.
Benefits of Loan Against Mutual Funds
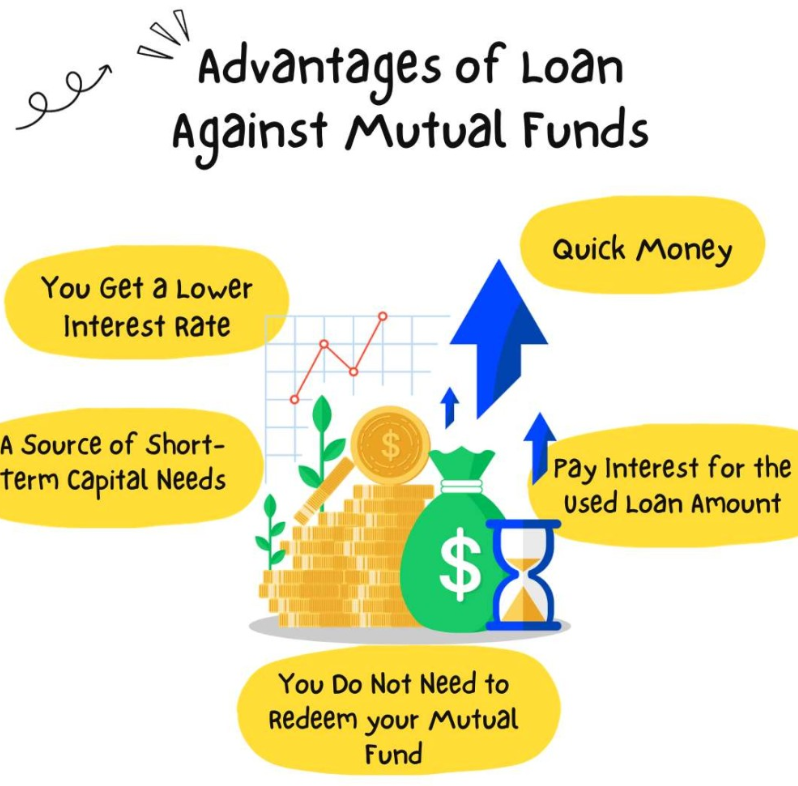
Liquidity without Disruption:
This is the primary advantage of LAMF. You access cash without selling your mutual funds, allowing your investments to continue growing potentially.
Lower Interest Rates:
Lenders typically offer lower interest rates on LAMFs compared to personal loans or credit cards. As a result, you can save significantly on borrowing costs especially when taking out larger loans.
Faster Processing:
Obtaining an LAMF is often quicker than applying for a fresh loan. The lender already has your investment details, streamlining the process.
Tax-deductible Interest:
You can potentially deduct the interest paid on a Loan Against Mutual Fund (LAMF) from your taxable income under Section 24(b) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. This benefit applies when you use the loan for specific purposes such as business expenses, investing in certain assets, or funding higher education. In contrast, if you redeem your mutual funds, you may have to pay capital gains tax, depending on the type and duration of your investment.
Equity Funds:
For equity funds held for less than 1 year, short-term capital gains are taxed at 15% (plus applicable surcharge and cess). Equity funds held for more than 1 year attract Long Term Capital Gains (LTCG) tax. If the LTCG exceeds Rs 1 lakh per year, a 10% tax with indexation benefit applies.
Debt Funds:
Short-term capital gains from debt funds are taxed according to your income tax slab. LTCG from debt funds are taxed at a flat rate of 20% with indexation benefit.
Example:
Imagine you invested INR 5 lakh in a mutual fund, and over time, it grows to INR 7 lakh. Then, an emergency expense of INR 2 lakh arises. Instead of redeeming your investment, you can opt for a LAMF. You simply borrow INR 2 lakh against your INR 7 lakh portfolio without selling any units. Meanwhile, your mutual fund continues to grow in value. Additionally, you may benefit from tax deductions on the interest paid for the loan.
Taxation
Equity Funds:
- If held for less than 1 year: 15% short-term capital gains tax
- More than 1 year: 10% long-term capital gains (LTCG) tax on gains over ₹1 lakh
Debt Funds:
- Short-term gains are taxed as per your income slab
- Long-term gains taxed at 20% with indexation
Example
Let’s say you invested ₹5 lakh in a mutual fund. It grows to ₹7 lakh. Suddenly, you need ₹2 lakh.
Instead of redeeming the fund, you can borrow ₹2 lakh as LAMF. You keep your ₹7 lakh invested. Your fund may continue to grow, and you may also save on taxes.
Things to Consider Before Opting for LAMF
- Margin Requirement: Lenders provide a percentage of your mutual fund’s value (typically 50-75%) as a loan. A market downturn could trigger a “margin call,” forcing you to either top up the margin or sell some of your holdings.
- Impact on Investment Returns: While you retain ownership of your mutual funds, the loan repayment obligation can impact your overall return on investment.
- Tax Implications: Consult a tax advisor to understand the tax treatment of interest paid on LAMF and any potential capital gains implications if you sell holdings to meet a margin call.
Is LAMF Right for You?
LAMF can be a valuable tool if used strategically. Here are some situations where LAMF might be a good fit:
- Short-term emergencies: For unexpected medical bills, urgent home repairs, etc., Loan Against Mutual Funds allows access to cash without disrupting your long-term investment goals.
- Funding short-term goals: Need funds for a down payment on a two-wheeler or a child’s school admission? You may find a LAMF to be a better option than liquidating your entire investment.
- Debt consolidation: If you have high-interest debt from credit cards or personal loans, consolidating it with a lower-interest LAMF can save you money. To get detailed guidance about LAMF click here.
Conclusion
Loan Against Mutual Funds offers a convenient way to access funds from your mutual funds without selling them. However, it’s crucial to understand the risks involved, like margin calls and potential tax implications. Carefully evaluate your financial situation and investment goals before opting for LAMF. Consulting a financial advisor can be extremely helpful in making an informed decision. To get instant cash, click here.
FAQs
What is a Loan Against Mutual Funds (LAMF)?
A Loan Against Mutual Funds is a way to borrow money by pledging your mutual fund units as collateral. You don’t sell your investments. Instead, you take a loan against them and your funds continue to stay invested.
How much loan can I get against my mutual fund units?
Typically, you can get 50% to 75% of your mutual fund’s current market value as a loan. However, the exact amount may vary depending on the type of mutual fund and the lender’s policy.
Is the interest rate on LAMF lower than personal loans?
Yes, most lenders offer lower interest rates on LAMFs compared to unsecured personal loans or credit cards. This makes LAMF a more cost-effective borrowing option.
Will I lose my mutual fund units if I take a loan?
No, your units stay invested and continue to grow. However, if the market falls and your portfolio value drops, you may get a margin call from the lender. If you don’t maintain the margin, some units might be sold.
Are there any tax benefits on a Loan Against Mutual Funds?
Yes, in some cases. If you use the loan for business, buying assets, or education, you may get a tax deduction. This applies to the interest paid under Section 24(b) of the Income Tax Act. But rules can vary, so it’s best to check with a tax expert.
